The View page displays a submission's general information and data. Ver vídeo
Información del envío
Número del envío: 1259
ID del envío: 1268
Submission UUID: 56706e08-ddc8-4cae-b5e8-8053d4b76ab1
Submission URI: /es/form/wizard-fichatraductologica
Created: Jue, 07/04/2022 - 15:12
Completed: Jue, 07/04/2022 - 15:14
Changed: Dom, 20/10/2024 - 10:27
Remote IP address: (desconocido)
Enviado por: HECTOR SEBASTIAN JANNE OROZCO LUYANDO
Idioma: Español
Is draft: No
Página actual: webform_confirmation
Form Ficha Terminológica: Ficha Traductológica
Término
Arterial wall
Inglés (Estados Unidos) (214)
Ciencias Biológicas, Químicas y de la Salud (403)
Médico Cirujano (422)
Cardiología
A layered structure consisting of the tunica intima (simple squamous epithelium surrounded by a connective tissue basement membrane with elastic fibers), tunica media (the smooth muscle that provides support for the vessel and changes vessel diameter to regulate blood flow and blood pressure) and tunica adventitia (which is the connective tissue with varying amounts of elastic and collagenous fibers).
National Cancer Institute. (2022). Classification & Structure of Blood Vessels. SEER Training Modules. Recuperado el 06 de abril de 2022, de https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/cardiovascular/blood/classification.html
Recent findings have helped to explain the fate of cholesterol entering the arterial wall. LDL can undergo both fusion and aggregation. These changes may cause increased retention of LDL in lesion connective tissue matrix and LDL uptake by macrophages. In the cornea, apparent fusion of LDL occurs in the absence of macrophages. Mast cells may be important in LDL fusion, as mast cell-derived proteases can induce fusion of LDL through proteolysis of apolipoprotein B. LDL in arterial wall atherosclerotic lesions was found to be sialic acid-poor and ceramide-enriched. These chemical changes promote LDL aggregation. Processes that may function to remove cholesterol from the arterial wall have been reported.
Kruth, H. S. (1997). The fate of lipoprotein cholesterol entering the arterial wall. En Current Opinion in Lipidology (Vol. 8, Issue 5, pp. 246–252). Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health). https://doi.org/10.1097/00041433-199710000-00002
Español
pared arterial
Nominal (221)
México (Mex.) (192)
Estructura fibrosa que forma las arterias, que son los conductos cilíndricos por los que circula la sangre al ir desde el corazón hasta los órganos del cuerpo. Está formada por diversas láminas superpuestas de distintos tipos de tejidos.
Medypsi - Noticias de Medicina y Psicología. (2022). Definición de pared arterial. Enciclopedia Salud. Recuperado el 06 de abril de 2022, de https://www.enciclopediasalud.com/definiciones/pared-arterial
Fueron evaluadas 45 mujeres diabéticas posmenopáusicas con edades comprendidas entre 50 y 65 años. La exploración ecográfica se realizó con un equipo Philips iE33 a Duplex-Doppler color con un transductor lineal de 7.5 MHz a nivel de las arterias carótidas. A cada paciente se le realizó el análisis de sangre para la determinación de factores bioquímicos. Se concluye que los triglicéridos y la hemoglobina glucosilada fueron los factores bioquímicos que más influencias tuvieron sobre los cambios macro y microvasculares de la pared arterial.
Caume, E., González, R., Guerra, L., Lacalle, I., Torres, M. (2017). Correlación de parámetros ecográficos y bioquímicos con el comportamiento mecánico de una pared arterial. VII Conferencia Internacional Ciencia y Tecnología por un Desarrollo Sostenible.
Multimedia
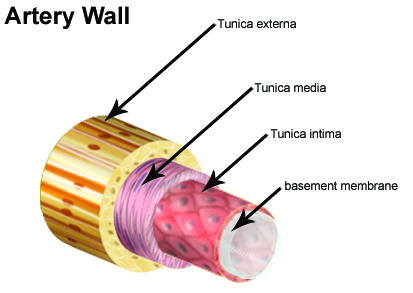
Externa
https://training.seer.cancer.gov/images/anatomy/cardiovascular/artery_wall.jpg
